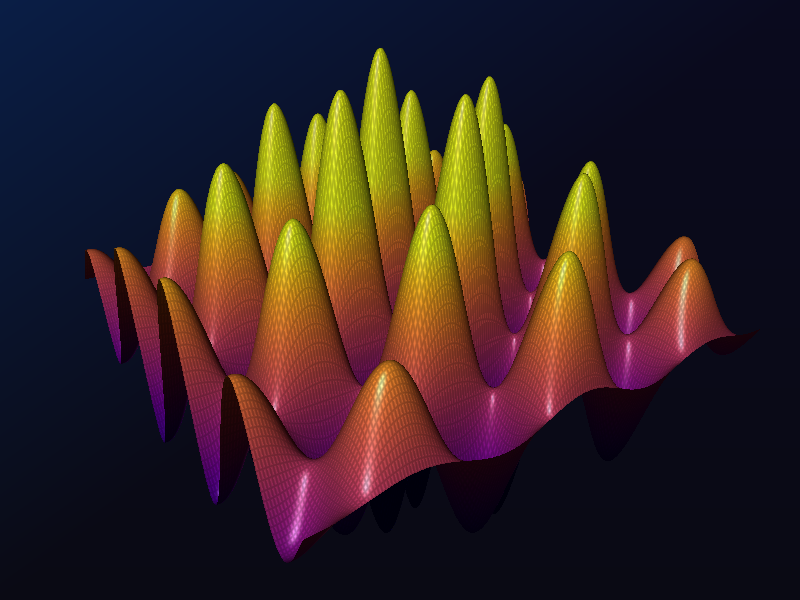
Surface plot¶
Show a rotating surface in 3D.
Tags: background, colormap, shape, arcball, mesh
import numpy as np
import datoviz as dvz
HAS_CONTOUR = True
# Grid parameters.
row_count = 200
col_count = row_count
# n = row_count * col_count
# Allocate heights and colors arrays.
grid = np.meshgrid(row_count, col_count)
shape = (row_count, col_count)
heights = np.zeros(shape, dtype=np.float32)
# Create grid of coordinates
x = np.arange(col_count)
y = np.arange(row_count)
xv, yv = np.meshgrid(x, y)
# Distances.
center_x = col_count / 2
center_y = row_count / 2
d = np.sqrt((xv - center_x) ** 2 + (yv - center_y) ** 2)
# Heights.
a = 4.0 * 2 * np.pi / row_count
b = 3.0 * 2 * np.pi / col_count
c = 0.5
hmin = -0.5
hmax = +0.5
heights = np.exp(-0.0001 * d**2) * np.sin(a * xv) * np.cos(b * yv)
# Colors.
colors = dvz.cmap('plasma', heights, hmin, hmax)
linewidth = 0.1
edgecolor = (0, 0, 0, 64)
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sc = dvz.ShapeCollection()
sc.add_surface(heights=heights, colors=colors, contour='edges')
app = dvz.App()
figure = app.figure()
panel = figure.panel(background=True)
arcball = panel.arcball(initial=(0.41, -0.95, 0))
camera = panel.camera(initial=(0, 0, 3))
visual = app.mesh(sc, lighting=True, contour=HAS_CONTOUR, linewidth=linewidth, edgecolor=edgecolor)
panel.add(visual)
app.run()
app.destroy()
sc.destroy()